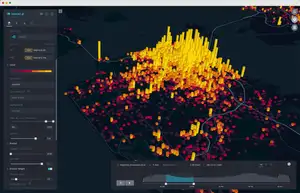
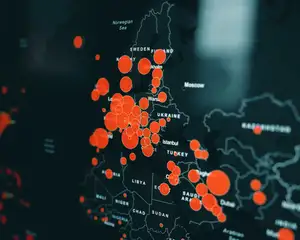
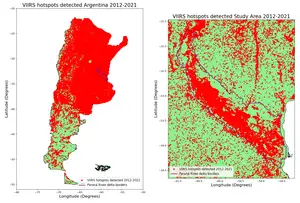
Maximize Preparedness for Natural Disasters by using a GIS to Perform Risk Assessments
In today's rapidly changing world, natural disasters are becoming increasingly frequent and more severe. This makes it imperative for individuals, communities, and businesses to be prepared for such events. Using a GIS (Geographic Information Systems) to perform a risk assessment is a powerful tool that can help organizations minimize the impact of natural disasters and plan for emergency response.
Understanding GIS Risk Assessment
GIS risk assessment is a process of using geospatial data and tools to identify, analyze, and map potential impacts of natural hazards such as earthquakes, hurricanes, floods, and fires. The goal of GIS risk assessment is to provide actionable information to decision makers, allowing them to prioritize resources and make informed decisions about preparedness and response efforts.
GIS risk assessments consider various factors such as the frequency, severity, and likelihood of natural hazards, as well as the vulnerability of populations and assets. This information is then used to create maps and other visual representations of the potential impacts of these events, including estimates of economic losses and human casualties.
Benefits of GIS Risk Assessment for Natural Disasters
GIS risk assessments offer a number of benefits for organizations that are concerned about the impact of natural disasters. Some of the most important benefits include:
- Improved preparedness: By mapping the potential impacts of natural disasters, organizations can prioritize their preparedness efforts and allocate resources more effectively.
- Better decision making: GIS risk assessments provide decision makers with the information they need to make informed decisions about emergency response and recovery efforts.
- Increased efficiency: By integrating geospatial data and analysis into disaster planning and response efforts, organizations can improve the efficiency of their operations and reduce the overall impact of natural disasters.
- Enhanced collaboration: GIS risk assessments can bring together different stakeholders and organizations to collaborate on disaster planning and response efforts, leading to more coordinated and effective response.
Steps to Implementing GIS Risk Assessment
Implementing a GIS risk assessment for natural disasters involves several key steps, including:
- Data collection: The first step in implementing a GIS risk assessment is to gather and process geospatial data, including information on natural hazards, demographics, infrastructure, and land use.
- Analysis: The next step is to analyze the data to identify areas of high risk and to estimate the potential impacts of natural disasters.
- Mapping: The results of the analysis are then used to create maps and other visual representations of the potential impacts of natural disasters.
- Communication and dissemination: The results of the GIS risk assessment should be communicated to decision makers, stakeholders, and the general public, allowing them to make informed decisions about preparedness and response efforts.
Conclusion
GIS risk assessment is a powerful tool for organizations to minimize the impact of natural disasters and plan for emergency response. By integrating geospatial data and analysis into disaster planning and response efforts, organizations can improve their preparedness, increase their efficiency, and enhance collaboration among stakeholders. If you want to maximize your preparedness for natural disasters, consider implementing a GIS risk assessment in your organization today.