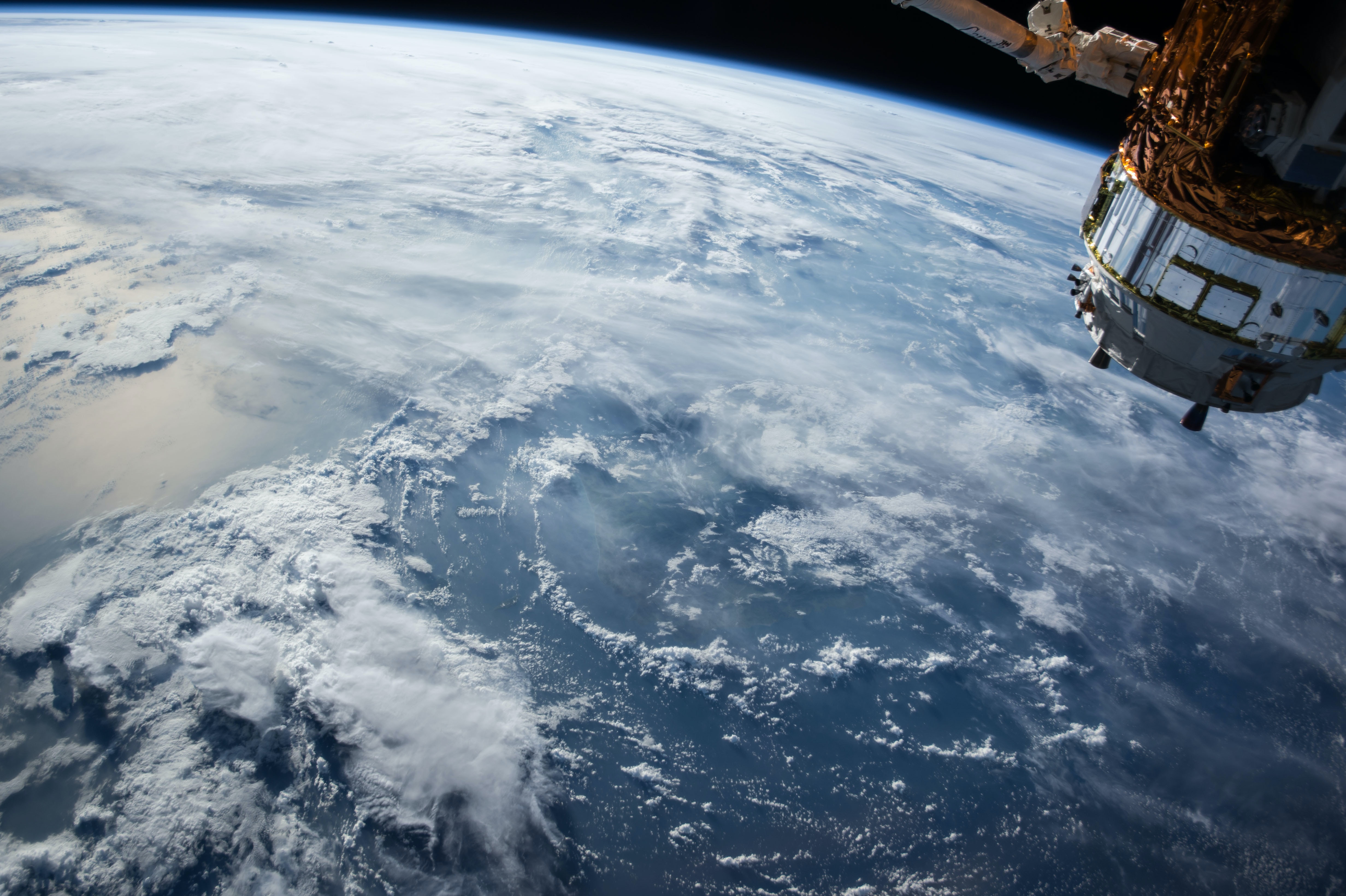
Unlocking the Potential of GIS in Remote Sensing
Unlock the potential of GIS in remote sensing. Learn how this technology is revolutionizing the way we understand and interact with the world.
Introduction
Geographic Information Systems (GIS) and remote sensing are two powerful technologies that have transformed the way we collect, analyze, and interpret spatial data. When combined, they offer unprecedented capabilities for monitoring and understanding our planet. This article will delve into the potential of GIS in remote sensing, providing a detailed guide on how this technology is revolutionizing the way we understand and interact with the world.

GIS and Remote Sensing: A Powerful Combination
GIS is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present all types of geographical data. On the other hand, remote sensing is the process of detecting and monitoring the physical characteristics of an area by measuring its reflected and emitted radiation at a distance from the targeted area. When combined, these two technologies provide a powerful tool for spatial data analysis.
GIS and remote sensing complement each other. While remote sensing provides a means to capture data from a distance, GIS provides the tools to analyze and visualize this data in a spatial context. This combination allows for detailed analysis of environmental conditions, land use changes, and various other phenomena.
The Role of GIS in Remote Sensing
GIS plays a crucial role in remote sensing by providing a platform for the integration, analysis, and visualization of remote sensing data. It allows for the overlay of different data layers, enabling a comprehensive analysis of spatial relationships and patterns. This integration of data can help in various fields such as environmental monitoring, urban planning, disaster management, and more.
GIS also plays a vital role in the processing and interpretation of remote sensing data. It can be used to correct, classify, and analyze remote sensing images. For instance, GIS can help in correcting distortions in remote sensing data due to the movement of the satellite or atmospheric conditions. It can also assist in classifying the data based on different land use categories or identifying changes over time.

Current Research and Developments
Recent research in the field of remote sensing has focused on developing more efficient and accurate methods for data analysis. One such development is the creation of a standardized catalogue of spectral indices, which are mathematical combinations of different spectral bands in a remote sensing image. These indices are used to enhance the visibility of specific features in an image, such as vegetation, water bodies, or urban areas.
A recent study published in the journal Scientific Data presents a standardized catalogue of 231 spectral indices, which are widely used in remote sensing. This catalogue includes indices for various application domains, including vegetation, water, burn, snow, urban, radar, soil, and kernel indices.
The standardization of spectral indices is a significant advancement in the field of remote sensing. It allows for the consistent use of these indices across different studies and applications, enhancing the comparability and reproducibility of results. Moreover, the use of standardized spectral indices can facilitate the automation of remote sensing data analysis, making it more efficient and accessible.
Use Cases of GIS in Remote Sensing
The potential of GIS in remote sensing is vast and varied. The following are some specific use cases that highlight the application of GIS and remote sensing in different fields.
Environmental Monitoring
One of the primary use cases of GIS and remote sensing is environmental monitoring. The standardized catalogue of spectral indices can be used to monitor various environmental parameters such as vegetation health, soil moisture, and water quality. For instance, vegetation indices can help in assessing the health and productivity of vegetation, which is crucial for agriculture and forestry. Similarly, water indices can be used to monitor the quality and extent of water bodies, which is vital for water resource management.
Urban Planning
GIS and remote sensing are also extensively used in urban planning. Urban indices from the spectral indices catalogue can help in mapping and monitoring urban areas. This can provide valuable insights into urban growth patterns, land use changes, and urban heat islands. Such information is crucial for sustainable urban planning and development.
Disaster Management
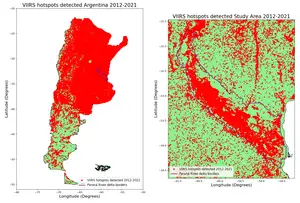
In the field of disaster management, GIS and remote sensing play a crucial role. Burn indices from the spectral indices catalogue can be used to assess the extent and severity of wildfires. Similarly, radar indices can be used in flood mapping and monitoring. This information can help in disaster response and recovery efforts, as well as in planning and preparedness for future disasters.
Automation of Remote Sensing Data Analysis
The standardization of spectral indices can also facilitate the automation of remote sensing data analysis. By using standardized indices, it is possible to develop automated algorithms for data processing and analysis. This can make remote sensing data analysis more efficient and accessible, opening up new possibilities for its application in various fields.
Conclusion
The combination of GIS and remote sensing offers a powerful tool for spatial data analysis. It allows for the integration, analysis, and visualization of remote sensing data, providing valuable insights into various phenomena. The recent advancements in the field, such as the standardization of spectral indices, further enhance the potential of GIS in remote sensing, paving the way for more efficient and accurate data analysis.
As we continue to face global challenges such as climate change, urbanization, and natural disasters, the role of GIS and remote sensing in understanding and addressing these issues becomes increasingly important. By unlocking the potential of GIS in remote sensing, we can better understand our world and make more informed decisions to protect and manage our resources effectively.